The WHOA Advantage: Meet the Cyber Secure Cloud PlatformTM from Whoa Networks
The WHOA Advantage: Meet the Cyber Secure Cloud PlatformTM from Whoa Networks
Enjoy a Fully Managed, Secure Cloud Infrastructure
Secure & Compliant Cloud Hosting Solutions
Secure Cloud
The Whoa Networks Cyber Secure Cloud Platform combines an enterprise-grade architecture featuring multiple Tier IV Data Centers. Including IDS & IPS…
Cybersecurity
Our comprehensive portfolio of cybersecurity solutions will protect your business from risks before cyber attacks and security breaches occur. Our team…
Professional Services
Our professional services team provides a start-to-finish methodology that unifies your mission-critical applications and infrastructure. We partner…
Assessments & Audits
WHOA’s assessment and audit services help organizations that are being asked to demonstrate compliance for SOC 1 and SOC 2 audits, ISO 27001, etc…
Disaster Recovery
Our fully managed Disaster Recovery solutions eliminate the complexity and cost for organizations having to build out redundant systems for BC/DR.
Penetration Testing
Penetration-testing your network is a proactive effort of protecting your network and business from risks before attacks or security breaches occur. Our experts…

Threat Detection & Prevention

Multi-Layered Security

Compliance PCI/HIPAA

Enterprise Architecture

Real Time Monitoring

Tier IV Data Centers
The WHOA Advantage
Far Beyond Commoditized Infrastructure
It takes ingenuity to create a cloud infrastructure with enterprise grade security, intrusion detection & prevention services, providing compliance readiness for business.
Meet the Cyber Secure Cloud PlatformTM from Whoa Networks

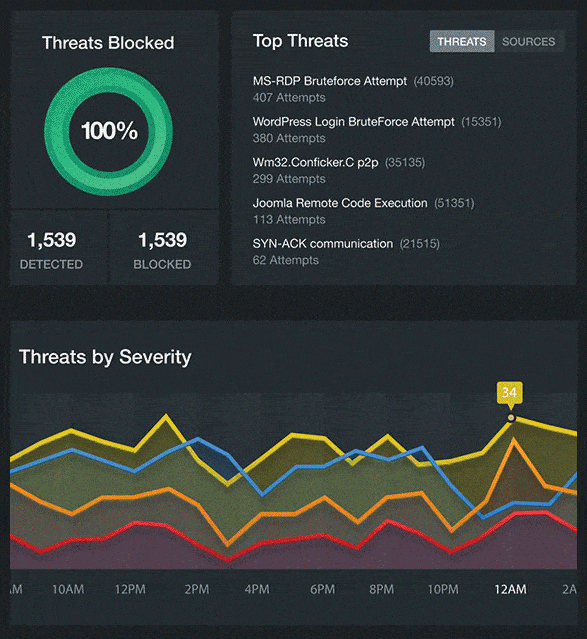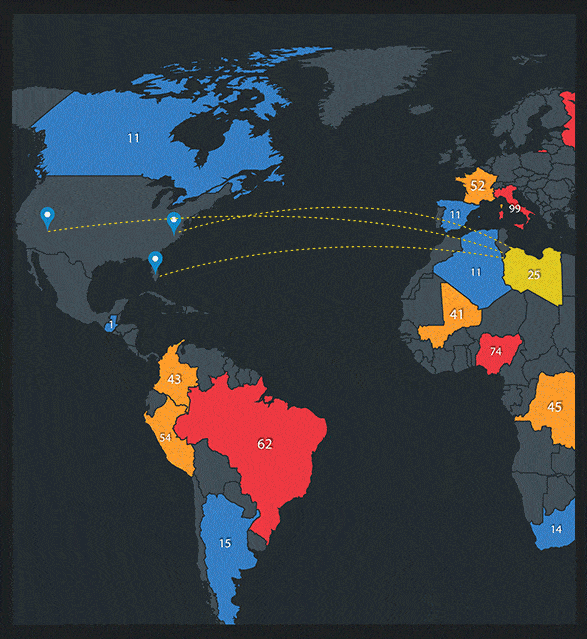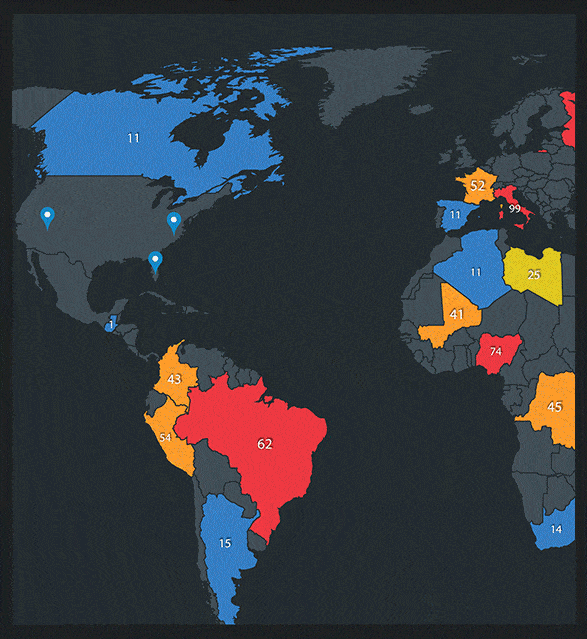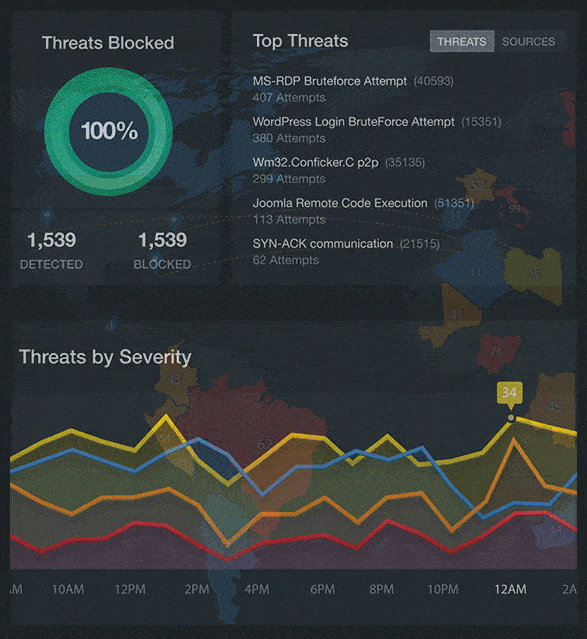
Real Time Visibility Into Your Cloud Security
When it comes to moving to the cloud, the advantages are clear, but what about cloud security? Watch this video to see what our next-generation secure cloud can do for your business.
Security and compliance for regulated industries.
The Whoa Networks enterprise secure cloud features a multi-layered approach to security and maps compliance requirements to our secure cloud solutions that mirror security best practices.

Ease of Doing Business
Tired of feeling like a number? We make it easy to do business with us.
Secure
We provide visibility and transparency into your cloud security and resource performance in real time.
Service
White glove support for Infrastructure as a Service, Security as a Service, and a host of Managed Services.
Experience
Our cloud experts provide secure cloud and compliant solutions for businesses both large and small.
Peace of Mind
Our enterprise-grade cloud platform features a multi-layered approach to security and compliance.
Experience a Live 10-minute Demo
See how the WHOA Cyber Secure Cloud Platform can take your IT to the next level in a live, personalized demo with a solution consultant.